2011 The former Hitachi Cable News Release
Information (including product prices, product specifications, details of services, launch dates, inquiry information, and URLs) contained in this news release is current as of the date of the press release but is subject to change without notice. Please note that details may differ from those effective on the search date.
Hitachi Cable succeeded research and development on pure copper
HiFC with high-purity copper potential and high functions
Hitachi Cable, Ltd. has announced successful research and development pure copper HiFC (purity of approximately 99.99% or more*1) amenable to continuous casting and hot rolling. This material offers various advantages, including almost same softening characteristic as high-purity 6N copper (approximately 99.9999%). This was achieved by adding trace amounts of titanium into commercial grade copper and by controlling copper impurities.
Electro-conductive materials are used across a broad range of applications, from large-scale, long-distance transmission to small-scale, high-speed transmission, as the materials to support the transmission and distribution of both information and energy. Copper is used for a superior electro-conductive material in numerous industries.
Hitachi Cable Group has succeeded mass production of oxygen-free copper (OFC) first in Japan and has also succeeded of invention and practical utility of supper fine copper-alloy wires. And we work from development of copper materials to mass production with casting, rolling, wire-drawing, cable-producing, and assembling process.
In recent years, materials with high electrical, thermal conductivity, long bending fatigue life time and excellent connection reliability are demanded in wide range market fields, including power electric field, medical instrument field, and information & telecommunication field. For these demands, materials including oxygen-free copper wire and high-purity copper wires are widely used effectively. To get such high-quality copper materials, reducing oxygen and impurities on tough pitch copper*2 were carried out. However, as the high-purity copper wire is extremely costly even though it has remarkable performance, its usage is limited, and therefore the development of more economical materials has been a new target.
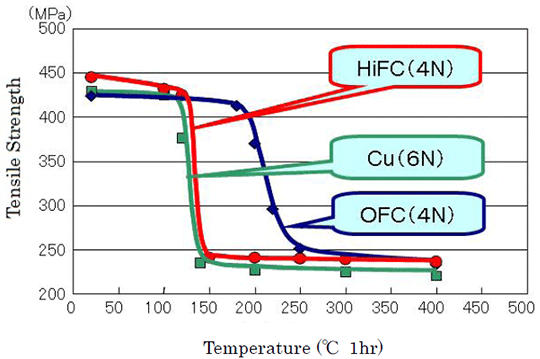
In this situation, Hitachi Cable has succeeded research and development on pure copper HiFC amenable to continuous casting and hot rolling. This material offers various benefits, including softening characteristics corresponding to that of highly pure copper (see Fig. 1), achieved by adding minute amounts of titanium.
Based on a research and development strategy, that departs from the conventional approach of focusing on reducing residual copper impurities, HiFC is designed to provide both excellent characteristics and cost performance. Trace amounts of titanium are added and thermo-mechanical treatment applied in order to catch trace amounts of sulfur in copper as compounds consist of titanium. In addition to superior elongation performance attributable to the formation of fine crystal grains, HiFC allows the formation of fine crystal gains on the surface layer of the conductor, conferring both softness and long bending fatigue life time.
Listed below are the six primary characteristics of HiFC.
Main characteristics of HiFC
| (1) | Low-temperature softening characteristic such as high-purity copper (see Fig. 1) |
| (2) | Superior elongation performance due to fine crystal grains formed by controlling metallurgical structures |
| (3) | Softness and long bending fatigue life time made possible by controlling metallurgical structure (see Fig. 2) |
| (4) | High conductivity (101% IACS or higher) |
| (5) | Remarkable welding performance equal to or exceeding that of oxygen-free copper wire |
| (6) | Highly cost-effective production through continuous casting and rolling |
In addition, after establishing mass-production technologies for HiFC, the Hitachi Cable Group are planning to seek for research and development to advance practical applications as a new generation electro-conductive material in various products, including wires, cables, and wiring materials.
Fig. 1: Softening characteristic of pure copper HiFC (2.6 mm diameter) as tested by Hitachi Cable Laboratory
Fig. 2: Metallurgical structure of fine crystal grains observed on surface of pure copper HiFC (tested by Hitachi Cable Laboratory)
| *1 | HiFC is currently in the process of registration as a registered trademark of Hitachi Cable, Ltd. in Japan. |
| *2 | Tough pitch copper refers to copper of Cu 99.90% or higher containing 0.02-0.05% oxygen. It is widely used as an electro-conductive material. |